
Through its notification dated 9 October 2020 the FSSAI has Gazette Notified the Food Safety and Standards Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Eighth Amendment Regulations, 2020 related to the provision of additional additives (sorbitan monostearate) and microbiological requirements for spices. These amendments shall come into force on the date of their publication in the Official Gazette and Food Business Operators shall comply with all the provisions of these regulations by 1st July, 2021.
In the Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011, –
In regulation 2.4 CEREALS AND CEREAL PRODUCTS
- In 2.4.1, clause 2 relating to “Fortified atta” shall be omitted
- In 2.4.2, clause 2 relating to “Fortified maida” shall be omitted.
In sub-regulation 2.9.30 EDIBLE COMMON SALT
- clause 2 relating to “IODISED SALT” shall be omitted.
- clause 3 relating to “IRON FORTIFIED COMMON SALT” shall be omitted.
- clause 5 relating to “Iron Fortified Iodized Salt (double fortified salt)” following standards and entries against thereof shall be omitted, namely:
In regulation 2.10, BEVERAGES, (Other than Dairy and Fruits & Vegetables based)
- sub-regulation 2.10.5 relating to “Beverage- ALCOHOLIC” shall be omitted.
In Appendix A, under the heading ―IV. USE OF FOOD ADDITIVES IN FOOD PRODUCTS
In table 5 relating to confectionary, in food category system, 5.2 Confectionery including hard and soft candy, nougats etc. other than food categories 5.1, 5.3, and 5.4 for Paraffin wax or liquid paraffin (food grade) the following shall be substituted, namely:
Food Additive INS Number Recommended maximum level Note
|
Food Additive |
INS Number |
Recommended maximum level |
Note |
|
Liquid paraffin |
905e |
GMP |
– |
In Table 7, relating to Bakery products,
Under the following Food Category Systems
7.1.2 Crackers
7.1.3 Other ordinary bakery products
7.1.4 Bread-type products, including bread stuffing and bread crumbs
7.1.5 Steamed breads and buns
7.1.6 Mixes for bread and ordinary bakery wares
The following food additive has been added in all above food categories
|
Food Additive |
INS Number |
Recommended maximum level |
Note |
|
SORBITAN ESTERS OF FATTY ACIDS |
|
10.000mg/kg |
11 |
In table 12 relating to Salts, spices, soups, salads and protein products in the Food Category System 12.8, Yeast and like products the following food additive has been included.
|
Food Additive |
INS Number |
Recommended maximum level |
Note |
|
Sorbitan monostearate |
491 |
10,000 mg/kg |
|
In Table 14, relating to Beverages, excluding dairy products in the Food Category System 14.1.2.1, Fruit juices (fruit juices for industrial use, thermally processed fruits juices) the following food additive has been added
|
Food Additive |
INS Number |
Recommended maximum level |
Note |
|
Nisin |
234 |
5,000 IU |
FS04b |
In the Food Category System against the entries relating to 14.1.4.3, Concentrates (liquid or solid) for water-based flavoured drinks (synthetic syrups for dispensers, sharbat (synthetic syrup) * squashes, crushes, fruit syrups, cordials and barley water the following entry “*The following additives permitted in synthetic syrups for dispensers” shall be substituted with
|
*The following additives permitted in synthetic syrups for dispensers |
127 |
In the same Food Category System 14.1.4.3, the entry *The following additives are permitted in sharbat (synthetic syrup)” will be substituted with the following
|
*The following additives are permitted in sharbat (synthetic syrup) |
127 |
in Table 15, relating to Ready-to–eat savouries, in the Food Category System 15.1, Snacks and savouries–potato, cereal, flour or starch based (from roots and tubers, pulses and legumes) the following food additives have been included
|
Food Additive |
INS Number |
Recommended Maximum Level |
|
Paprika oleoresin |
160c(i) |
GMP |
|
Curcumin |
100(i) |
GMP |
|
Turmeric |
100(ii) |
GMP |
In the Notes to the Food Additives mentioned in the Table 1 to 15, the following Note and entry have been added
|
Note |
Notes to the Food Additives mentioned in the Table 1 to 15 |
|
No |
|
|
FS04b |
For use in pre-packed coconut water only |
In Appendix B relating to “Microbiological Requirements” for the TABLE 3 relating to “Microbiological Parameters for Spices‘ and the entries relating thereto, the following table and the entries shall be substituted, namely:-
Table: 3 Microbiological Standards for Spices and Herbs
Table -3 A Microbiological Requirements for Spices and Herbs –Process
Hygiene Criteria
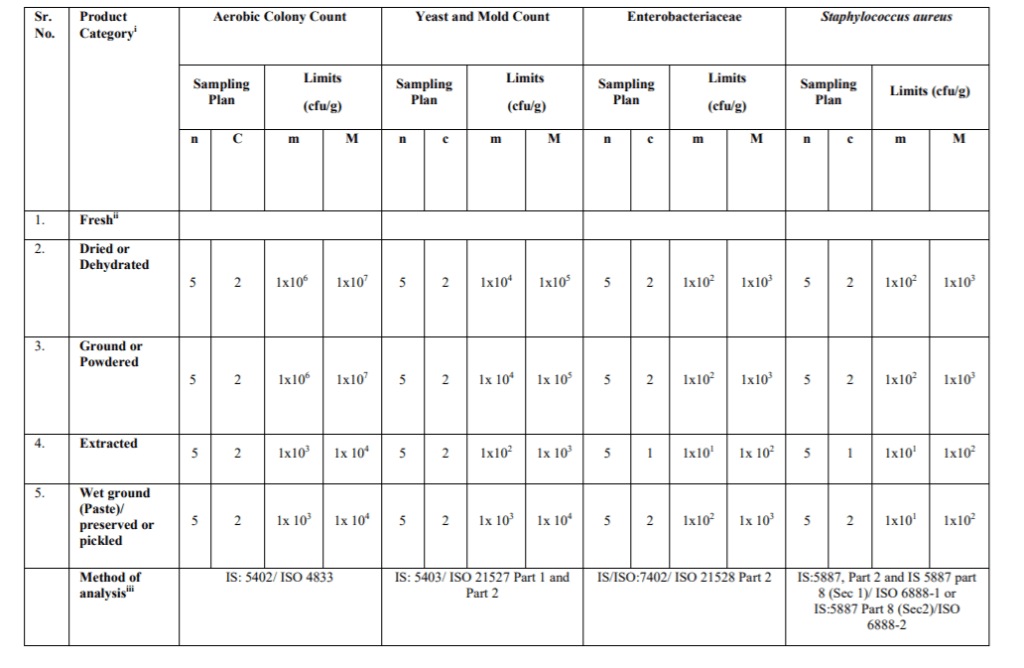
Table -3 B Microbiological Requirements for Spices and Herbs – Food Safety Criteria
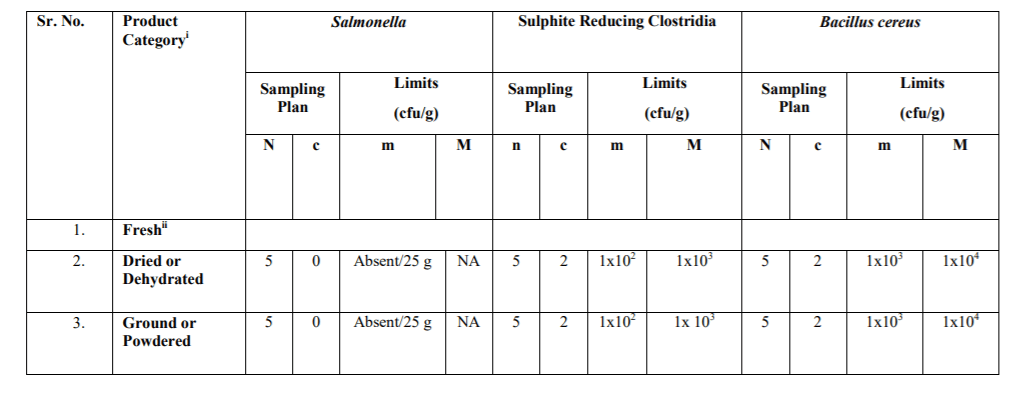
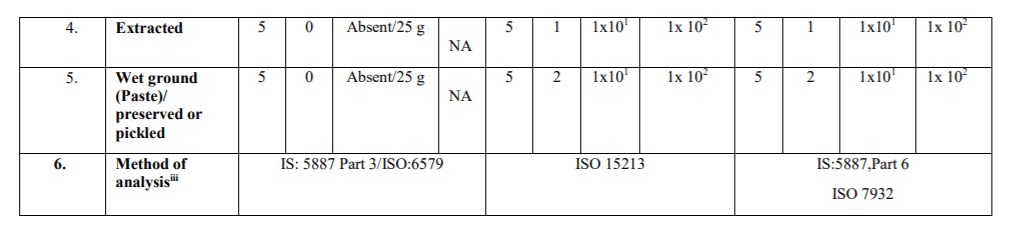
NA-Not applicable
- Definitions:
- Fresh: The spices and herbs that are consumed fresh.
- Dried or dehydrated: The product obtained by drying/removal of most of the moisture by any suitable method which ensures characteristics of fresh spices on rehydration or pre-cooking.
- Ground or powdered: Ground or powdered product obtained by grinding or crushing of clean dried/dehydrated fruits, capsules, buds, seeds, rhizomes, aril, kernel, berries and stigmas etc.
- Extracted: Products of the spices and herbs which are produced by extracting in a concentrated form including oleoresins.
- Wet ground (paste)/preserved or pickled: Semi solid, preserved product using brine, vinegar and other permitted preservatives or physical methods.
For detailed product definition, refer to Food Safety & Standards (Food Product Standards & Food Additives) Regulations, 2011.
- The category – “Fresh” shall be regulated in accordance with the Good Manufacturing Practices and Code of Good Hygiene Practices notified under Schedule4 of FSS (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations, 2011.
Stage where the Microbiological Standards shall apply:
The microbiological standards with respect to the product categories specified in Table-3A (Process Hygiene Criteria) indicate the acceptable functioning of the production process. These are not to be used as requirements for releasing the products in the market. These are indicative values above which corrective actions are required in order to maintain the hygiene of the process in compliance with food law. These shall be applicable at the end of the manufacturing process. The Microbiological Standards in Table-3B (Food Safety Criteria) define the acceptability of a batch/lot and shall be met in respect of the products at the end of manufacturing process and the products in the market during their shelf- life.
Action in case of unsatisfactory result:
In case of non-compliance in respect of Process Hygiene Criteria specified in Table- 3A, the FBO shall:
- check and improve process hygiene by implementation of guidelines in Schedule 4 of FSS (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations; and,
- Ensure that all food safety criteria as specified in Table -3B are complied with.
Sampling Plans and Guidelines;
For Regulator: The sampling for different microbiological standards specified in Table-3A and 3B shall be ensured aseptically at manufacturing units and/or at retail points, as applicable, by a trained person with specialized knowledge in the field of microbiology following guidelines in the Food Safety and Standards (Food Products and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011 and ISO: 707 (Latest version). The samples shall be stored and transported in frozen condition at -18°C(±2°C) or under refrigerated conditions at 2-5°C as applicable except the products that are recommended to be stored at room temperature by the manufacturer to enable initiation of analysis within 24 hours of sampling. Preservatives shall not be added to sample units intended for microbiological examination. The desired number of sample units as per sampling plan given in Table-3A & 3B shall be taken from same batch/lot and shall be submitted to the notified laboratory. Three sets, each containing ‘n‘ number of samples (n as defined in the sampling plan e.g if n=5, then total no. of samples to be drawn is 15) shall be drawn. Each of these three sets shall be tested in three different accredited laboratories. The final decision shall be based on the results of three accredited laboratories. In the case of food safety criteria (Table 8B), results from all the three laboratories should indicate compliance with specified criteria. There will be no provision for retesting or resampling for microbiological testing. The testing in laboratory shall be ensured as per reference test methods given below in reference test methods for regulatory compliance.
For FBO: Food Business Operator (FBO) shall perform testing as appropriate as per the microbiological standards in Table-3A & 3B to ensure validation and verification of compliance with the microbiological requirements. FBO shall decide themselves subject to minimum prescribed under FSSR (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses), the necessary sampling and testing frequencies to ensure compliance with the specified microbiological requirements. FBO may use analytical methods other than those described in reference test methods given below for in-house testing only. However, these methods shall not be applicable for regulatory compliance purpose.
Interpretation of Results:
|
2-Class Sampling Plan (where n, c and m are specified) |
3-Class Sampling Plan (where n, c, m and M are specified) |
|
1. Satisfactory, if all the values observed are ≤ m 2. Unsatisfactory, if one or more of the values observed are >m |
1. Satisfactory, if all the values observed are ≤ m 2. Acceptable, if a maximum of c values are between m and M. 3. Unsatisfactory, if one or more of the values observed are > M or more than prescribed c values are >m |
iii. Reference test methods: The following test methods shall be applied as reference methods. Test methods prescribed in FSSAI Manual of Method of Analysis of Foods (Microbiological Testing) may also be referred along with the IS/ISO methods specified for Process Hygiene Criteria and Food Safety Criteria. Latest version of test methods shall apply. In case where an ISO method adopted by the BIS is specified (e.g IS XXXX/ISO YYYY), latest version of the ISO method (or its BIS equivalent, if available) shall apply.
|
S. N |
Parameter |
Reference Test Methods |
|
1. |
Aerobic Plate Count |
Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the enumeration of microorganisms — Part 1: Colony count at 30 °C by the pour plate technique IS 5402/ISO:4833 |
|
2. |
Yeast and Mould Count |
Method for Yeast and Mould Count of Food Stuffs and Animal feed- IS 5403 Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuff-Horizontal method for the enumeration of yeasts and moulds-Part1: Colony count technique in products with water activity greater than 0.95-ISO 21527-1 Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuff-Horizontal method for the enumeration of yeasts and moulds-Part2: Colony count technique in products with water activity less than 0.95-ISO 21527-2 |
|
3. |
Enterobacteriaceae |
Microbiology – General Guidance for the Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae without Resuscitation – MPN Technique and Colony-count Technique- IS/ISO 7402 Microbiology of Food and Animal feeding stuff –Horizontal methods for the detection and enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae- Part 2: Colony- count method ISO 21528-2 |
|
4. |
Staphylococcus aureus |
Methods for detection of bacteria responsible for food poisoning: Part 2 Isolation, identification and enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus and faecal streptococci- IS 5887 Part 2 Methods for Detection of Bacteria Responsible For Food Poisoning Part 8 Horizontal Method For Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci/ (Staphylococcus aureus and other species) Section 1 Technique using baird-parker agar medium – IS 5887 (Part 8/Sec 1:/ ISO 6888-1:1999 Methods For Detection Of Bacteria Responsible For Food Poisoning Part 8 Horizontal Method For Enumeration Of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci/ (Staphylococcus aureus And Other Species) Section 2 Technique using rabbit plasma fibrinogen agar medium– IS 5887 (Part 8/Sec 2)/ISO 6888-2: 1999 |
|
5. |
Salmonella |
Methods for Detection of Bacteria Responsible for Food Poisoning – Part 3: General Guidance on Methods for the Detection of Salmonella- IS 5887: Part 3 Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs — Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp.- ISO6579 |
|
6. |
Sulfite-Reducing Bacteria |
Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs — Horizontal method for the enumeration of sulfite-reducing bacteria growing under anaerobic conditions ISO 15213 |
|
7. |
Bacillus cereus |
Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs-Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Preservative Bacillus Cereus, Part 6 Colony –count Technique at 30°C- IS 5887-6 Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs-Horizontal method for the enumeration of presumptive Bacillus cereus-Colony- count technique at 30degrees C.-ISO 7932 |
Source : FSSAI
Hemant Sharma says
Please provide a write up after every category of additives so that a layman can understand the reason behind the FSSAI amendments.
FSH Team says
Dear Hemant Ji,
Thanks for writing to us. Your suggestion is taken, appreciate your time.